Get a user access token
Learn how to get user access tokens, including getting your authorization code, requesting and getting your token, and using a refresh token.
You have a Swan project and you have access to your Dashboard.
After getting a user access token (step 4), use it immediately to verify which user is logged in (step 5).
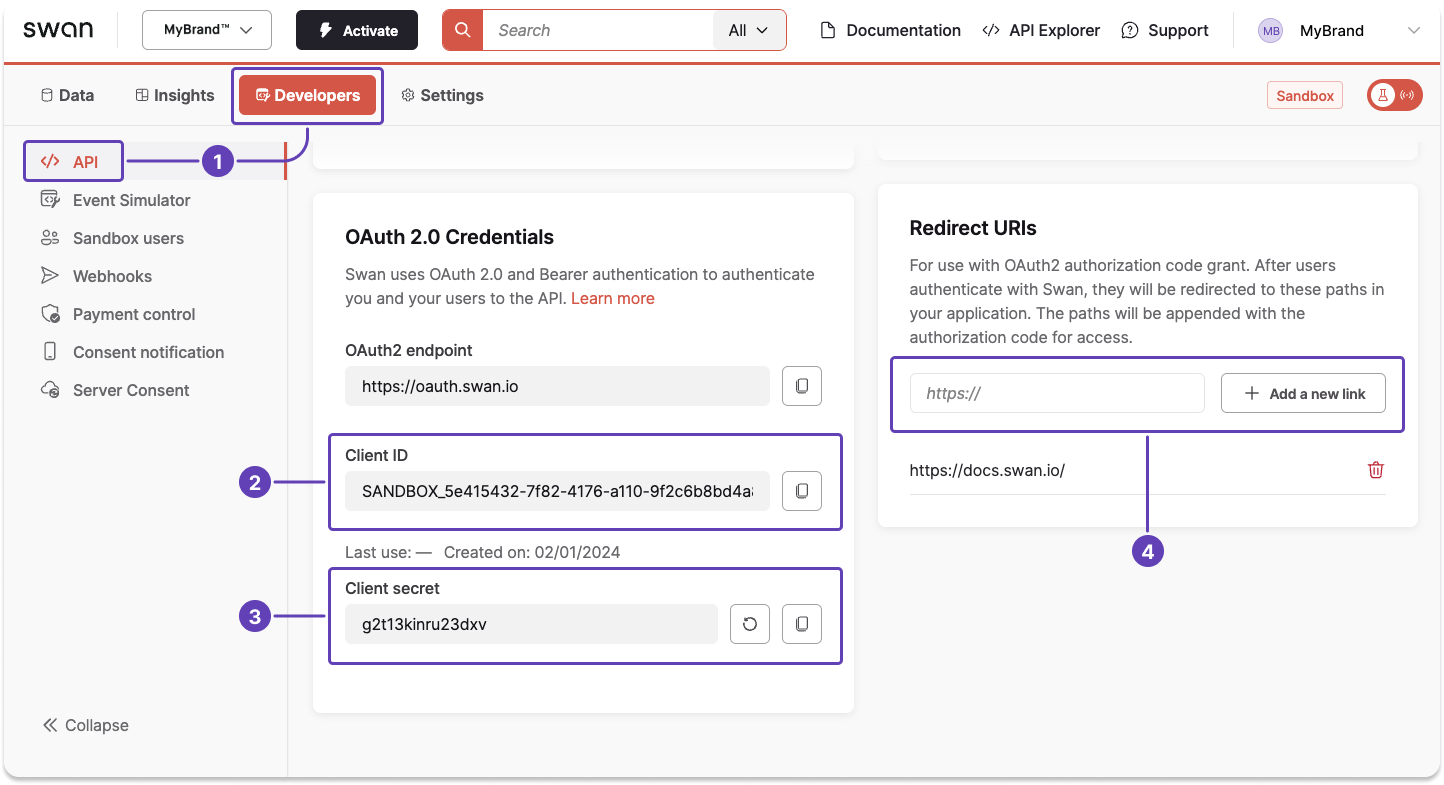
Step 1: Get your credentials and add a redirect URI
- Go to Dashboard > Developers > API.
- Locate your client ID.
- Locate your client secret, or generate a new secret if needed.
- Enter your redirect URI, then click + Add a new link.
Keep this page open; you'll need these values for subsequent steps.
Step 2: Get an authorization code
You need an authorization code to request a user access token.
Follow steps 2.1 through 2.3 to get your code. Note that authorization codes are single-use.
2.1 Construct authorization URL
Construct a URL with the required query parameters, adding any optional parameters you'd like. Query parameters are case sensitive.
- Review the example URL in the code block. Note that the example features hard returns for readability, which you should remove before sharing your URL.
- Add your client ID and redirect URI to your URL.
- Add any optional parameters to the end of your URL following the model
¶meter=value. - Send the URL to your user.
# Model
¶meter=value
# Spaced-out example
https://oauth.swan.io/oauth2/auth?
response_type=code
&client_id=$YOUR_CLIENT_ID
&redirect_uri=$YOUR_REDIRECT_URI
&scope=openid%20offline
&state=kdqsjdlkjsqdlkqjsdlkjsqd
&onboardingId=$ONBOARDINGID_OF_YOUR_CUSTOMER
&accountMembershipId=$ACCOUNTMEMBERSHIPID_OF_YOUR_CUSTOMER
&identificationLevel=Auto
&firstName=Jules
&lastName=Fleury
# Example URL including the `onboardingId`
https://oauth.swan.io/oauth2/auth?response_type=code&client_id=$YOUR_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=$YOUR_REDIRECT_URI&scope=openid%20offline&state=kdqsjdlkjsqdlkqjsdlkjsqd&onboardingId=$ONBOARDINGID_OF_YOUR_CUSTOMER&identificationLevel=Auto&firstName=Jules&lastName=Fleury
# Example URL including the `accountMembershipId`
https://oauth.swan.io/oauth2/auth?response_type=code&client_id=$YOUR_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=$YOUR_REDIRECT_URI&scope=openid%20offline&state=kdqsjdlkjsqdlkqjsdlkjsqd&accountMembershipId=$ACCOUNTMEMBERSHIPID_OF_YOUR_CUSTOMER&identificationLevel=Auto&firstName=Jules&lastName=Fleury
Required parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
response_type=code(line 6) | Initiates the authorization code flow. |
client_id(line 7) | Public identifier for the Swan app, obtained from your Dashboard in step 1. |
redirect_uri(line 8) | Specifies where the authorization server should send the user after approval, added to your Dashboard in step 1. |
scope=openid%20offline(line 9) | Defines the requested scopes for the user authorization.
|
state(line 10) | A value to be retransmitted in the query string when redirecting back to you. |
Optional parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
onboardingId(line 11) | Avoids asking the customer to enter their own residence address if they provide that information during onboarding. |
email | If you include the email parameter, it triggers an email verification flow automatically. If you include the parameter and the email address, it triggers the email verification flow with the email address pre-filled.Email addresses must be encoded, for example email=jules%40email.com. |
identificationLevel(line 13) | Indicate your preferred identification level: PVID, QES, Expert or Auto.Swan recommends setting Auto as your preferred identification level when guiding users through an identification flow, reengaging them to complete it, or inviting account members.Auto allows Swan to direct your users to the best identification flow for their situation. If your project is configured to bypass identification, eligible users will automatically skip it.If you use the Auto identification level, make sure you include the onboardingId (line 11) or the accountMembershipId (line 12) in the authorization URL. |
phoneNumberfirstName(line 14) lastName(line 15) birthDatebirthCitybirthCountrynationalitylanguagebirthPlacePostalCoderesidencyAddressresidencyAddressCityresidencyAddressCountryresidencyAddressPostalCode | Avoids asking the customer to enter this information during user registration. Required formats:
|
2.2 Receive approval from user
If you didn't send your authorization URL to your user, send it now.
When clicked, the URL opens an authorization page explaining how to connect with Swan and why the user's phone number is required.
- If the user is on a mobile device, they validate their phone number with a 6-digit code sent by Swan in a text message.
- If the user is using a computer, they enter their phone number, then receive a link on their mobile phone that opens a browser.
You can choose to display the authorization page in fullscreen or as a native popup. A native popup is more challenging to implement but provides a better user experience.
Note that you can't use webviews or iFrames. Read about why in the overview of the integrate Strong Customer Authentication guide.
2.3 Receive authorization code
If the user approves the request, the authorization server redirects the browser back to your redirect URI. Your authorization code expires 10 minutes after being created, so use it immediately to request your user access token.
- Copy the full URL from your browser. It contains your authorization code and state in the query string.
- Confirm that the
statein the URL matches the initial state to protect against Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) and related attacks.
# Full URL
https://$YOUR_REDIRECT_URI?code=$YOUR_AUTHORIZATION_CODE&state=kdqsjdlkjsqdlkqjsdlkjsqd
# Spaced-out example
https://$YOUR_REDIRECT_URI?
code=$YOUR_AUTHORIZATION_CODE
&state=kdqsjdlkjsqdlkqjsdlkjsqd
Step 3: Request your access token
To get your user access token, send a cURL request with the following information:
- The user authorization code you received in step 2 (line 2).
- Your client ID and secret from your Swan Dashboard, explained in step 1 (lines 3-4).
- The URI you added to your Swan Dashboard in step 1 (line 5).
curl -v -X POST <https://oauth.swan.io/oauth2/token> \\
-d "code=$YOUR_AUTHORIZATION_CODE" \\
-d "client_id=$YOUR_CLIENT_ID" \\
-d "client_secret=$YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET" \\
-d "redirect_uri=$YOUR_REGISTRATED_URI" \\
-d "grant_type=authorization_code"
Step 4: Get your access token
Assuming the information provided was correct, you'll receive a response with a user access token.
The user access token is encoded.
After it's decoded, you can use the sub field to identify the user. The sub in the id_token represents the userID. In Sandbox, this is the Sandbox userID.
The example response explains that you're receiving a bearer token, which is a cryptic string, and that the token provides user-level access for one hour. The token scope lets you know you can use the token for OpenID Connect purposes.
The response also provides a refresh token that you can use one time to extend the validity of your user access token. Store the refresh token to use later.
{
"access_token": "$YOUR_USER_ACCESS_TOKEN",
"expires_in": 3600,
"id_token": "$YOUR_ID_TOKEN",
"refresh_token": "$YOUR_USER_REFRESH_TOKEN",
"scope": "openid offline",
"token_type": "bearer"
}
If your request returns an error, your authorization code from step 2 might already be expired, or your client secret might be invalid. Use a new authorization code or a new client secret (or both) to try your request again.
Step 5: Verify which user is logged in
After getting the token, use it immediately to verify which user is logged in.
Adding a phoneNumber to the OAuth 2.0 URL in step 2.1 isn't sufficient to know which user is logged in.
Sometimes, a phone number might have been used by a deactivated user before being used for a new user.
Additionally, your user might have replaced the number you provided with a different number, or gone through the process to update their phone number with Swan.
It's impossible to detect these changes when getting a user access token, so it's crucial to verify that the user associated with the token is the logged-in user.
Use the user access token to run this query in the API Explorer and retrieve the associated userID.
Step 6: Refresh your access token
Consider using impersonation because:
- You don't need to manage or refresh user access tokens.
- You can use a project access token with a
userIDto perform user-level actions. - It helps maintain security while creating a smoother user experience.
When your user access token expires, you can use the refresh token provided in the cURL response to extend the usage of your user access token. Please note that while they don't expire, refresh tokens are single-use.
To refresh your user access token, send a cURL request to the same endpoint as step 3 with the following information:
- The refresh token you received in step 4 (line 2).
- Your client ID and secret from your Swan Dashboard, retrieved in step 1 (lines 3-4).
curl -v -X POST <https://oauth.swan.io/oauth2/token> \\
-d "refresh_token=$YOUR_REFRESH_TOKEN" \\
-d "client_id=$YOUR_CLIENT_ID" \\
-d "client_secret=$YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET" \\
-d "grant_type=refresh_token"
The response is the same as in step 4, but with a new refresh token. Store the new refresh token to use later, but delete the refresh token you already used because refresh tokens are single-use.
{
"access_token": "$YOUR_USER_ACCESS_TOKEN",
"expires_in": 3600,
"id_token": "$YOUR_ID_TOKEN",
"refresh_token": "$YOUR_USER_REFRESH_TOKEN",
"scope": "openid offline",
"token_type": "bearer"
}
If your refresh request returns an error, your single-use refresh token might have been used already, or your client secret might be invalid.
- First, generate a new secret on your Dashboard and try your request again.
- If your request still returns an error, your refresh token isn't working. Return to step 2 of this guide to get a new user access token.